Large asteroid to pass by Earth on Newroz
Technology 10:35 AM - 2021-03-14
.
The largest asteroid to pass by Earth this year will approach within about 1.25 million miles (2 million kilometers) of our planet on March 21, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) said Thursday.
March 21 is the first day of the Kurdish new year and is called Newroz. The term Newroz is derived from (New Roz) which means a new day in English. It is celebrated every year by Kurds, where people go out for picnics in nature and wear bright colored Kurdish clothes and dance on Kurdish music. On the eve of Newroz, in southern and eastern Kurdistan, bonfires are lit. These fires symbolize the passing of the dark season, winter, and the arrival of spring, the season of light.
The U.S. space agency said it would allow astronomers to get a rare close look at an asteroid.
The asteroid, 2001 FO32, is estimated to be about 3,000 feet (915 meters) in diameter and was discovered 20 years ago, NASA said.
"We know the orbital path of 2001 FO32 around the sun very accurately,” said Paul Chodas, director of the Center for Near Earth Object Studies. “There is no chance the asteroid will get any closer to Earth than 1.25 million miles.”
That is roughly 5.25 times the distance from Earth to the moon, but still close enough for 2001 FO32 to be classified as a “potentially hazardous asteroid.”
NASA said 2001 FO32 would pass by at 77,000 mph (124,000 kph), faster than the speed at which most asteroids encounter Earth.
“Currently, little is known about this object, so the very close encounter provides an outstanding opportunity to learn a great deal about this asteroid,” said Lance Benner, principal scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Reflections to be studied
NASA said astronomers hope to get a better understanding of the asteroid's size and a rough idea of its composition by studying light reflecting off its surface.
“When sunlight hits an asteroid's surface, minerals in the rock absorb some wavelengths while reflecting others,” NASA said. “By studying the spectrum of light reflecting off the surface, astronomers can measure the chemical 'fingerprints' of the minerals on the surface of the asteroid."
Amateur astronomers in some parts of the globe should be able to conduct their own observations.
“The asteroid will be brightest while it moves through southern skies,” Chodas said.
“Amateur astronomers in the Southern Hemisphere and at low northern latitudes should be able to see this asteroid using moderate-size telescopes with apertures of at least 8 inches in the nights leading up to closest approach, but they will probably need star charts to find it,” he said.
NASA said more than 95% of near-Earth asteroids the size of 2001 FO32 or larger have been cataloged and none of them has any chance of impacting our planet over the next century.
PUKmedia / VOA News
More news
-
German Forces Commander Ended his Mission at Mam Jalal's Grave
12:28 PM - 2024-04-23 -
Golden Bla Awards Ceremony Takes Place in Sulaymaniyah
11:32 AM - 2024-04-23 -
PUK Official: PUK is Committed to Holding Elections on Time
11:04 AM - 2024-04-23 -
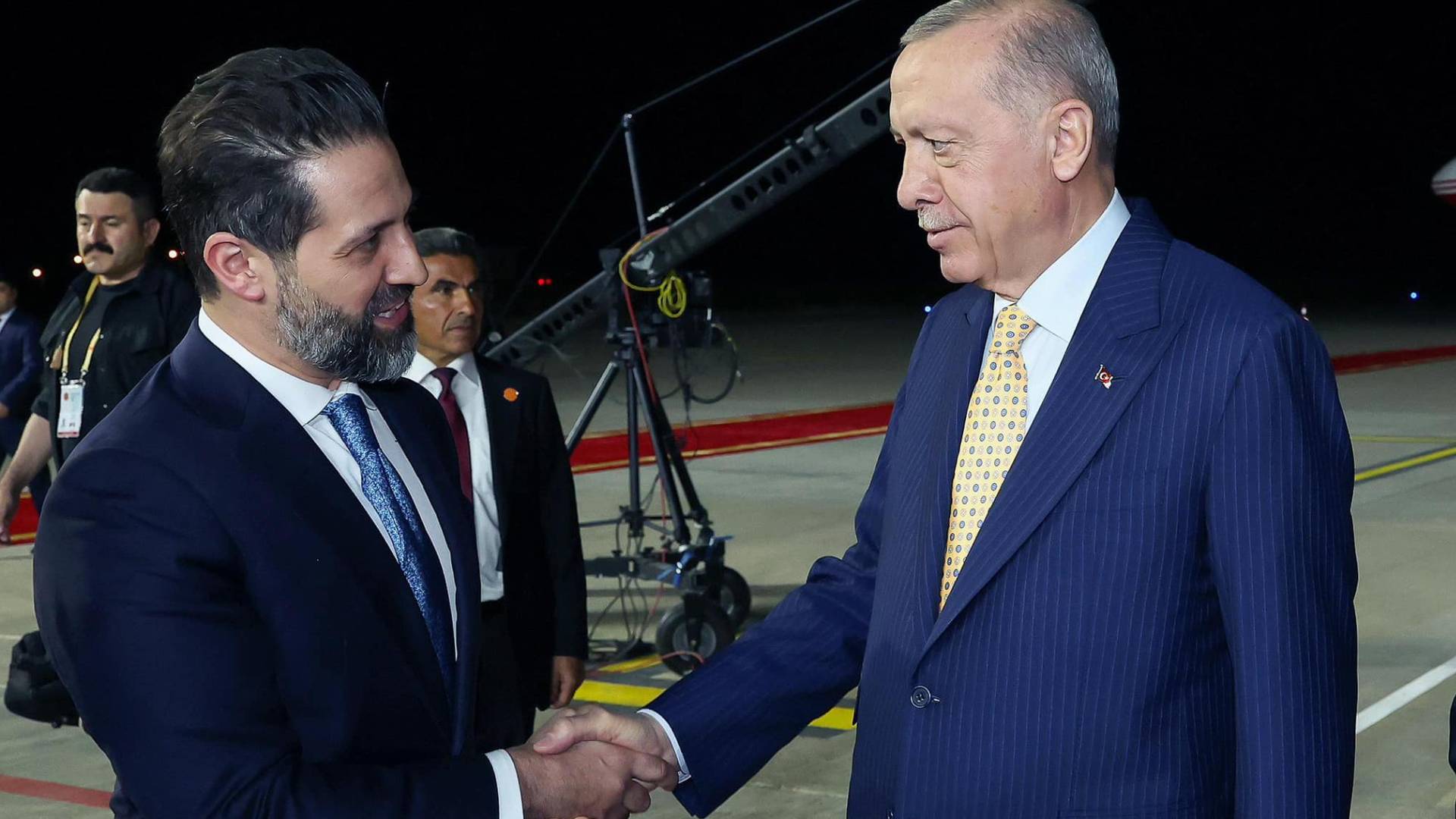
Turkish President Meets Kurdish Officials in Erbil
10:42 AM - 2024-04-23
see more
U.S. State Department Mentions the Deterioration of Journalists' Rights in Iraq & Kurdistan
06:48 PM - 2024-04-25
10 Notable Individuals Receive Golden Bla Award
09:27 PM - 2024-04-23
DPM Talabani Asks Turkish President to Lift Ban on Sulaymaniyah Airport
11:43 AM - 2024-04-23
Iraqi & Turkish Presidents: Problems Should Be Resolved Through Dialogue
05:00 PM - 2024-04-22
Most read
-
U.S. State Department Mentions the Deterioration of Journalists' Rights in Iraq & Kurdistan
Reports 06:48 PM - 2024-04-25 -
Another International Report Mentions Kurdistan's Limited Freedom
Reports 09:24 PM - 2024-04-25




.jpg)
 Application
Application